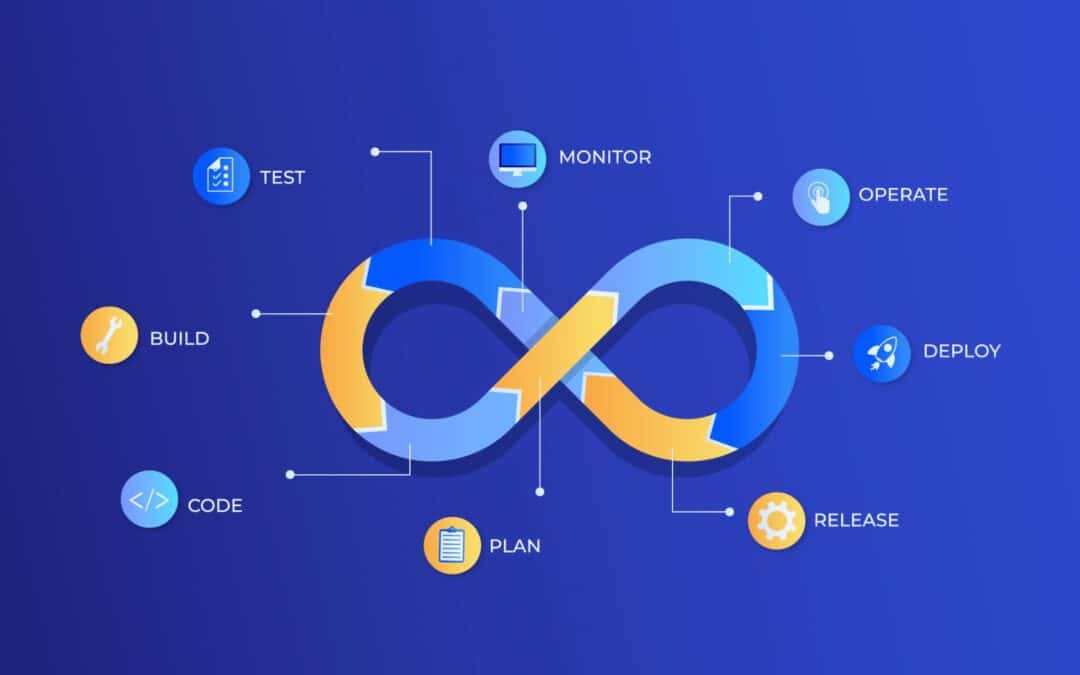
DevOps best practices have changed the software development world, with 99 percent of organizations seeing positive effects from their implementation. Teams using these practices achieve remarkable results. Elite teams now release software 208 times more often and 106 times faster than teams at the bottom.
The DevOps world keeps changing faster as we approach 2026. Market projections show growth at 19.7% yearly, reaching $25.5 billion by 2028. Many development and operations teams still find it hard to make DevOps work well. Our experience shows successful DevOps methods put resilience first, not just speed. The 2024 DORA report backs this up – the best teams excel at staying resilient.
In this article, we will share what really works, based on our 10 years of implementing DevOps strategies in organizations of all sizes. We’ll get into proven DevOps practices that show real results, from continuous integration to security measures.
What DevOps Best Practices Mean
DevOps best practices describe a structured DevOps approach that aligns development and operations teams across the entire development lifecycle. These best practices combine DevOps principles, agile project management, and a strong cultural shift toward shared responsibility, allowing teams to manage the software development lifecycle with speed and stability. The goal of DevOps transformation focuses on continuous improvement, faster software delivery, and meeting changing market demands.
Effective DevOps practices rely on CI CD, continuous integration, continuous delivery, and a reliable DevOps pipeline. Automation tools, automated tests, integration tests, version control, and code repositories help DevOps teams protect code quality, reduce cognitive load, and prevent introducing bugs during the development cycle. These DevOps processes improve deployment frequency, system performance, and operational efficiency.
Strong security measures remain essential throughout the DevOps lifecycle. Teams must incorporate security early, apply security testing, security checks, access controls, and continuous monitoring to fix vulnerabilities early. Monitoring systems, real-time monitoring, and incident response ensure optimal performance, protect the production environment, and drive long-term DevOps success through continuous feedback and customer feedback.
Core Principles Of DevOps
DevOps principles define how modern organizations align people, processes, and technology across the entire development lifecycle. These principles help development and operations teams deliver reliable software faster while maintaining software quality, strong security measures, and long-term operational excellence.
Collaboration And Shared Responsibility
DevOps succeeds when development teams, operations teams, security teams, and the QA team operate with shared responsibility. Clear ownership across the software development process reduces silos and improves trust between team members. Each role contributes to the same outcome rather than isolated tasks.
This principle improves incident response, simplifies project management, and strengthens operational efficiency. Close collaboration also creates faster feedback from customer feedback and internal stakeholders. When teams align goals, DevOps success becomes measurable through better deployment frequency, fewer security issues, and consistent delivery across the production environment.
Automation Across The DevOps Lifecycle
Automation sits at the core of modern DevOps best practices. Automation tools reduce manual effort in configuration management, infrastructure components, testing, and deployment. This approach improves consistency across the development cycle and limits human error.
Automated workflows support CI CD, continuous integration, integration tests, and automated tests. These capabilities help teams manage frequent code changes without sacrificing stability. Strong automation also supports operational efficiency, allowing teams to increase scalability while meeting evolving market demands with confidence.
Continuous Integration And Delivery
Continuous integration and continuous delivery ensure that application code moves smoothly from source code to release. Frequent commits to code repositories supported by version control improve transparency and reduce risk within the DevOps pipeline.
This principle improves software delivery speed while maintaining code quality. Small, frequent releases simplify troubleshooting and reduce the impact of failures. When CI CD pipelines remain reliable, teams can deliver quality software, respond to change faster, and maintain stable system performance.
Continuous Monitoring And Feedback
Reliable DevOps systems depend on continuous monitoring and real-time monitoring across applications and infrastructure. Monitoring systems provide visibility into performance, errors, and user behavior within the production environment.
A strong feedback loop helps teams detect issues early and optimize performance. Metrics such as latency, error rates, and usage patterns guide smarter decisions. This approach supports continuous improvement, improves software quality, and ensures the product environment is based on real usage rather than assumptions.
Security Built Into DevOps Processes
Security must exist throughout the DevOps lifecycle, not as a final checkpoint. Teams should incorporate security early through security testing, security checks, and automated scans within CI CD pipelines. Early action helps fix vulnerabilities early before release.
This principle reduces security breaches and strengthens the software supply chain. Strong access controls, secure code repositories, and regular audits protect both data and systems. When security becomes part of daily workflows, teams reduce risk without slowing software development.
Continuous Improvement And Learning
DevOps relies on an iterative approach that values learning over perfection. Teams review outcomes, analyze failures, and refine DevOps processes using the right metrics. This mindset supports long-term digital transformation.
Regular retrospectives reduce cognitive load and improve team confidence. Feedback from incidents, releases, and users shapes better decisions across the development lifecycle. A culture of improvement helps organizations adapt to evolving needs while sustaining performance and reliability.
Toolchain Alignment And Right Metrics
Success depends on selecting the right tools that fit workflows rather than adding complexity. DevOps tools should support visibility, automation, and collaboration across teams and systems.
Metrics must reflect outcomes such as software quality, deployment frequency, operational efficiency, and recovery time. Clear measurement supports better project management decisions and prevents wasted effort. When tools and metrics align, teams reduce friction and focus on delivering value through a mature DevOps approach.
10 DevOps Best Practices
DevOps best practices help organizations balance speed, stability, and security across the entire development lifecycle. These practices guide development and operations teams toward reliable software delivery, better collaboration, and continuous improvement while meeting evolving market demands.
Build A Strong DevOps Culture
A successful DevOps approach starts with culture, not tools. Development and operations teams must share responsibility across the software development lifecycle. Clear communication, mutual trust, and aligned goals remove silos that slow progress and create friction during delivery.
This cultural shift improves project management and supports operational excellence. Team members understand how their work affects system performance, software quality, and customer experience. When teams value collaboration, incident response improves and accountability becomes clear across the devops lifecycle.
Leadership support plays a critical role in long-term devops success. Managers should encourage transparency, learning, and ownership rather than blame. A strong culture allows teams to adapt quickly to change, reduce cognitive load, and deliver quality software that supports evolving business needs.
Automate Repetitive Processes
Automation remains a cornerstone of DevOps best practices. Manual tasks within configuration management, testing, and deployment often lead to errors and slow delivery. Automation tools create consistent workflows that reduce risk across the development cycle.
Automated tests, integration tests, and deployment scripts support frequent code changes without compromising stability. CI CD pipelines allow DevOps teams to release updates faster while maintaining code quality and operational efficiency. These systems also support higher deployment frequency and predictable software delivery.
Automation frees teams to focus on improvement rather than routine work. This approach strengthens the software development process, improves system reliability, and helps organizations respond faster to market demands while maintaining control over infrastructure components.
Adopt Continuous Integration And Delivery
Continuous integration and continuous delivery form the backbone of modernizing software. Frequent commits to code repositories supported by version control reduce integration risk and improve visibility across development teams.
CI CD pipelines validate application code through automated tests and security checks before release. Smaller release cycles reduce failure impact and simplify troubleshooting within the production environment. This practice improves software delivery speed without sacrificing quality.
Teams that adopt DevOps practices around CI CD gain confidence in releases and improve collaboration across operations teams and QA teams. Reliable pipelines help organizations meet customer expectations while supporting long-term DevOps transformation.
Manage Infrastructure As Code
Infrastructure as code brings consistency and control to infrastructure components. Configuration files define environments in a repeatable way, reducing drift between development, testing, and production systems.
This practice supports faster provisioning and reliable recovery during incident response. Infrastructure changes follow the same review process as application code, improving traceability and accountability across DevOps teams.
Infrastructure as code improves operational efficiency and system performance. Teams reduce manual configuration errors and maintain stable environments throughout the entire development lifecycle, which leads to better software quality and predictable releases.
Monitor Systems Continuously
Continuous monitoring ensures visibility across applications, services, and infrastructure. Monitoring systems provide real-time monitoring data on latency, errors, and resource usage within the production environment.
This visibility supports faster issue detection and informed decision-making. Teams respond quickly to anomalies before users experience disruption, which protects customer trust and software quality.
A strong feedback loop from monitoring data supports continuous improvement. Metrics guide optimization efforts and help teams maintain optimal performance while scaling services to meet evolving needs.
Integrate Security From The Start
Security must exist throughout the DevOps lifecycle rather than as a final step. Teams should incorporate security early through security testing, automated security checks, and access controls within CI CD pipelines.
Early security testing helps fix vulnerabilities early and reduces development cost. Secure code repositories, dependency checks, and software supply chain reviews protect application code from common security issues.
This practice reduces security breaches and strengthens trust across development teams and security teams. Security-first DevOps processes support stable software delivery without slowing development velocity.
Use Version Control Effectively
Version control supports collaboration, traceability, and accountability within DevOps teams. Centralized code repositories allow team members to track changes, review source code, and resolve conflicts efficiently.
Clear branching strategies reduce risk during the development cycle and support parallel work streams. Version control also enables rollback during incidents, which improves incident response and system stability.
Effective version control improves code quality and supports reliable CI CD pipelines. This practice strengthens the software development lifecycle and ensures teams maintain control over frequent code changes.
Measure The Right Metrics
Metrics guide decision-making across the DevOps approach. Teams should track indicators such as deployment frequency, recovery time, error rates, and system performance rather than vanity metrics.
The right metrics align technical work with business goals and market demands. Data-driven insights help teams identify bottlenecks and optimize processes across the DevOps pipeline.
Clear measurement supports operational excellence and continuous improvement. Teams gain visibility into progress and maintain focus on outcomes that improve software quality and customer satisfaction.
Enable Continuous Feedback
Continuous feedback connects users, teams, and systems throughout the development lifecycle. Customer feedback, monitoring insights, and team reviews create a reliable feedback loop.
This practice helps DevOps teams adjust feature priorities and improve the software development process. Feedback from production systems highlights performance gaps and usability issues early.
Organizations that value feedback deliver better software delivery outcomes. Teams adapt quickly, reduce waste, and align releases with real user needs.
Choose The Right DevOps Tools
Tools support DevOps practices but never replace process or culture. DevOps tools should integrate smoothly across CI CD, monitoring systems, AI automation tools, and configuration management.
Tool alignment reduces friction and cognitive load for team members. Integrated platforms improve visibility across development teams and operations teams.
The right tools support operational efficiency, optimal performance, and long-term DevOps success. Careful selection ensures technology enables teams rather than slowing progress across the entire development lifecycle.
Common DevOps Mistakes And How Best Practices Fix Them
Many DevOps failures come from process gaps rather than technology limits. Understanding common DevOps mistakes helps development and operations teams apply DevOps best practices correctly, improve software delivery, and protect software quality across the entire development lifecycle.
Lack Of Team Collaboration
A frequent DevOps mistake involves poor collaboration between development teams, operations teams, and security teams. Separate goals and unclear ownership create delays, miscommunication, and conflict during the software development lifecycle.
DevOps best practices fix this issue through shared responsibility and aligned objectives. Cross-functional collaboration improves project management and supports faster incident response. When teams communicate openly, software delivery becomes predictable, and system performance remains stable across environments.
Overreliance On Manual Processes
Manual workflows slow the DevOps pipeline and increase the risk of errors. Configuration management, testing, and deployment performed by hand often lead to inconsistent environments and production issues.
Automation tools solve this problem by standardizing DevOps processes. Automated tests, integration tests, and CI CD pipelines reduce human error and support frequent code changes. Automation improves operational efficiency while maintaining code quality and reliable releases.
Late Security Implementation
Security applied at the final stage of delivery exposes applications to serious security issues. Late security testing allows vulnerabilities to reach the production environment and increases the risk of security breaches.
DevOps best practices incorporate security early through security checks, security testing, and access controls. Early security testing helps fix vulnerabilities early and strengthens the software supply chain without slowing software development.
Poor Monitoring And Visibility
Limited monitoring systems reduce visibility into application behavior and infrastructure components. Teams often discover issues only after users report failures, which damages trust and software quality.
Continuous monitoring and real-time monitoring address this gap. Monitoring systems provide actionable insights that improve incident response and support optimal performance. Strong visibility helps DevOps teams maintain stability and continuous improvement.
Ignoring Feedback Loops
Teams that overlook customer feedback and internal feedback lose opportunities for improvement. Without a feedback loop, DevOps processes fail to adapt to market demands and evolving needs.
DevOps best practices emphasize continuous feedback from users, monitoring data, and team reviews. Feedback guides better decisions, improves software delivery, and aligns development priorities with real business value.
Weak Version Control Practices
Inconsistent version control leads to code conflicts, lost changes, and unstable releases. Poor management of source code increases risk during the development cycle.
Strong version control practices fix this issue by maintaining clear commit histories and controlled access to code repositories. Reliable version control improves code quality, supports CI CD pipelines, and simplifies incident response.
Wrong Metrics And Tool Choices
Many teams track metrics that fail to reflect DevOps success. Vanity metrics and disconnected DevOps tools increase cognitive load and reduce operational efficiency.
DevOps best practices focus on the right metrics, such as deployment frequency, recovery time, and system performance. Careful tool selection supports DevOps transformation and helps teams maintain long-term operational excellence.
How GainHQ Supports DevOps Best Practices
GainHQ supports DevOps best practices by centralizing communication, visibility, and feedback across development and operations teams. Clear conversation history, shared inboxes, and structured workflows reduce silos and improve collaboration throughout the software development lifecycle. Teams manage incidents, customer feedback, and internal requests from one platform, which improves operational efficiency and incident response.
GainHQ also strengthens continuous feedback and monitoring efforts. Support tickets, user issues, and feature requests create a reliable feedback loop that connects real customer needs with DevOps teams. This insight helps teams fix vulnerabilities early, improve software quality, and optimize system performance.
By aligning support data with DevOps processes, GainHQ helps teams deliver stable software faster, adapt to evolving needs, and maintain long-term DevOps success without adding unnecessary complexity.
FAQs
Do DevOps Best Practices Work For Small Teams?
Yes. DevOps best practices scale well for small teams when processes stay simple and focused. Even lean development and operations teams can improve software delivery, code quality, and operational efficiency by adopting CI CD, automation tools, and shared responsibility early.
Can DevOps Best Practices Reduce Deployment Risks?
Yes. DevOps best practices reduce risk by promoting smaller code changes, continuous integration, automated tests, and reliable DevOps pipelines. These practices improve visibility across the development lifecycle and help teams detect issues before they reach the production environment.
Do DevOps Practices Require Expensive Tools?
No. DevOps success depends more on process and culture than on tool cost. Many DevOps tools offer open-source or affordable options that support version control, monitoring systems, automation, and configuration management without increasing cognitive load.
Is DevOps Only Relevant For Cloud-Based Teams?
No. DevOps practices apply to both on-premise and cloud environments. Infrastructure components, CI CD workflows, security testing, and continuous monitoring improve software quality regardless of deployment model.
Does DevOps Replace Traditional Project Management?
No. DevOps complements project management rather than replacing it. Agile project management aligns well with DevOps principles by supporting continuous feedback, faster software delivery, and adaptive planning across the entire development lifecycle.
How Long Does A DevOps Transformation Take?
DevOps transformation varies by organization size and maturity. Teams often see early improvements in deployment frequency and incident response within months, while long-term operational excellence develops through continuous improvement and learning.
Can DevOps Best Practices Improve Customer Experience?
Yes. DevOps best practices improve customer experience by enabling faster releases, better system performance, and rapid response to customer feedback. Continuous delivery and real-time monitoring help teams meet evolving needs with stable, high-quality software.